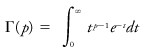Gamma distribution: Difference between revisions
From Glossary of Meteorology
(Created page with " {{TermHeader}} {{TermSearch}} <div class="termentry"> <div class="term"> == gamma distribution == </div> <div class="definition"><div class="short_definition">A contin...") |
m (Rewrite with Template:Term and clean up) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Term | |||
|Display title=gamma distribution | |||
{{ | |Definitions={{Definition | ||
{{ | |Num=1 | ||
|Meaning= | |||
A continuous [[random variable]] ''x'' is said to have a gamma distribution if the [[range]] of ''x'' consists of all positive real numbers and if ''x'' possesses a [[density function]] ''f''(''x'') that satisfies the equation <blockquote>[[File:ams2001glos-Ge3.gif|link=|center|ams2001glos-Ge3]]</blockquote> where β and ''p'' are positive numbers and where Γ is the gamma function defined by the integral <blockquote>[[File:ams2001glos-Ge4.gif|link=|center|ams2001glos-Ge4]]</blockquote> for p > 0. <br/> The mean of the density function is β''p'', and the [[standard deviation]] is β(''p'')<sup>½</sup>. The gamma distribution, which is a special case of the [[Pearson distribution]], is skewed to the right. In meteorology, [[scalar]] multiples of the gamma distribution are used to represent size distributions of [[cloud drops]]. <br/>''See'' [[skewness]]. | |||
}} | |||
}} | |||
Latest revision as of 07:37, 29 March 2024
A continuous random variable x is said to have a gamma distribution if the range of x consists of all positive real numbers and if x possesses a density function f(x) that satisfies the equation
The mean of the density function is βp, and the standard deviation is β(p)½. The gamma distribution, which is a special case of the Pearson distribution, is skewed to the right. In meteorology, scalar multiples of the gamma distribution are used to represent size distributions of cloud drops.
See skewness.
where β and p are positive numbers and where Γ is the gamma function defined by the integral
for p > 0.
The mean of the density function is βp, and the standard deviation is β(p)½. The gamma distribution, which is a special case of the Pearson distribution, is skewed to the right. In meteorology, scalar multiples of the gamma distribution are used to represent size distributions of cloud drops.
See skewness.