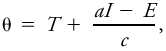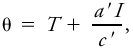Sol-air temperature: Difference between revisions
From Glossary of Meteorology
(Created page with " {{TermHeader}} {{TermSearch}} <div class="termentry"> <div class="term"> == sol–air temperature == </div> <div class="definition"><div class="short_definition">T...") |
m (Rewrite with Template:Term and clean up) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Term | |||
|Display title=sol–air temperature | |||
{{ | |Definitions={{Definition | ||
|Num=1 | |||
|Meaning=The [[temperature]] that, under conditions of no [[direct solar radiation]] and no air motion, would cause the same [[heat transfer]] into a house as that caused by the interplay of all existing atmospheric conditions. | |||
|Explanation=It is given by the formula <blockquote>[[File:ams2001glos-Se35.gif|link=|center|ams2001glos-Se35]]</blockquote> where θ is the sol–air temperature, ''T'' the outdoor [[air temperature]], ''a'' the radiational [[absorptivity]] of the wall surface, ''I'' the incident [[radiation]], ''c'' the coefficient of convective heat transfer between air and building material, and ''E'' the difference between the [[longwave radiation]] emitted and received by the surface. In practice, this equation has been reduced to <blockquote>[[File:ams2001glos-Se36.gif|link=|center|ams2001glos-Se36]]</blockquote> where θ, ''T'', and ''I'' are the <br/>''same as'' above; ''a''′ is a constant for construction material; and ''c''′ is a constant for [[climate]].<br/> Landsberg, H. E. 1954. Bioclimatology of housing. Recent Studies in Bioclimatology, Meteor. Monogr.. 2(8). p. 86. | |||
}} | |||
}} | |||
Latest revision as of 07:14, 30 March 2024
The temperature that, under conditions of no direct solar radiation and no air motion, would cause the same heat transfer into a house as that caused by the interplay of all existing atmospheric conditions.
It is given by the formula
same as above; a′ is a constant for construction material; and c′ is a constant for climate.
Landsberg, H. E. 1954. Bioclimatology of housing. Recent Studies in Bioclimatology, Meteor. Monogr.. 2(8). p. 86.
where θ is the sol–air temperature, T the outdoor air temperature, a the radiational absorptivity of the wall surface, I the incident radiation, c the coefficient of convective heat transfer between air and building material, and E the difference between the longwave radiation emitted and received by the surface. In practice, this equation has been reduced to
where θ, T, and I are the
same as above; a′ is a constant for construction material; and c′ is a constant for climate.
Landsberg, H. E. 1954. Bioclimatology of housing. Recent Studies in Bioclimatology, Meteor. Monogr.. 2(8). p. 86.