Fundamental dimensions: Difference between revisions
From Glossary of Meteorology
(Created page with " {{TermHeader}} {{TermSearch}} <div class="termentry"> <div class="term"> == fundamental dimensions == </div> <div class="definition"><div class="short_definition">Ther...") |
m (Rewrite with Template:Term and clean up) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Term | |||
|Display title=fundamental dimensions | |||
{{ | |Definitions={{Definition | ||
|Num=1 | |||
|Meaning=There are seven basic dimensions in science, from which all other dimensions are derived (Table 1); two supplementary dimensions are listed in Table 2. | |||
|Explanation=Historically, a variety of units have been used as measures of each dimension (e.g., length units: meters, inches, nautical miles, light years). One set has been adopted as the international system ([[SI]]) of units. The first letters of the first three units of this international system are "m, k, s"; hence, this system of units is sometimes called the MKS system. Derived units are formed from combinations of basic units. Examples of some derived units that are used in meteorology are listed in Table 3. A prefix (Table 4) can be added to these units to indicate larger or smaller values, such as kilometer (km), which is 1000 m.<br/> [[File:ams2001glos-Ft2.gif|link=|center|ams2001glos-Ft2]][[File:ams2001glos-Ft3.gif|link=|center|ams2001glos-Ft3]][[File:ams2001glos-Ft4.gif|link=|center|ams2001glos-Ft4]][[File:ams2001glos-Ft5.gif|link=|center|ams2001glos-Ft5]] | |||
}} | |||
= | }} | ||
Latest revision as of 12:26, 30 March 2024
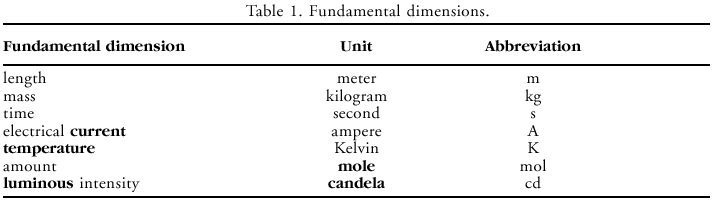
There are seven basic dimensions in science, from which all other dimensions are derived (Table 1); two supplementary dimensions are listed in Table 2.
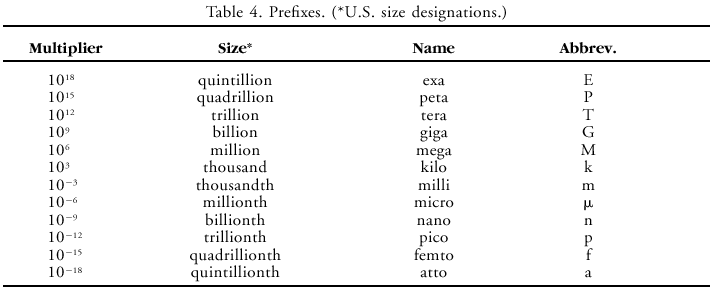
Historically, a variety of units have been used as measures of each dimension (e.g., length units: meters, inches, nautical miles, light years). One set has been adopted as the international system (SI) of units. The first letters of the first three units of this international system are "m, k, s"; hence, this system of units is sometimes called the MKS system. Derived units are formed from combinations of basic units. Examples of some derived units that are used in meteorology are listed in Table 3. A prefix (Table 4) can be added to these units to indicate larger or smaller values, such as kilometer (km), which is 1000 m.