Eddy flux: Difference between revisions
From Glossary of Meteorology
No edit summary |
m (Rewrite with Template:Term and clean up) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Term | |||
|Display title=eddy flux | |||
{{ | |Definitions={{Definition | ||
|Num=1 | |||
|Meaning=(''Or'' turbulent flux.) The rate of [[transfer]] of a conservative fluid property through a surface by turbulent [[eddies]]. | |||
|Explanation=In the case of an unchanging mean state, the eddy flux of a property ''S'' in the ''z'' direction is expressed by <blockquote>[[File:ams2001glos-Ee2.gif|link=|center|ams2001glos-Ee2]]</blockquote> where lower case represents [[turbulence]] values (fluctuations from the mean), ''w'' represents [[vertical velocity|vertical velocity]], ρ [[density]], and the bar represents the mean over a chosen period. By analogy with [[molecular diffusion]], the eddy flux in the [[planetary boundary layer]] is often expressed by <blockquote>[[File:ams2001glos-Ee3.gif|link=|center|ams2001glos-Ee3]]</blockquote> where ''K''<sub>''s''</sub> is the turbulent transfer coefficient (also [[turbulent exchange]] coefficient, or [[eddy diffusivity]]). This can be generalized to include [[eddy diffusion]] in the horizontal (''x'', ''y'') plane. If ''S'' is replaced by ''c''<sub>''p''</sub>''T'', where ''c''<sub>''p''</sub> represents [[specific heat]] at constant [[pressure]] and ''T'' represents [[temperature]], the vertical turbulent [[heat flux]] (or eddy heat flux) can be represented by <blockquote>[[File:ams2001glos-Ee4.gif|link=|center|ams2001glos-Ee4]]</blockquote> where θ is the temperature fluctuation, ''K''<sub>''h''</sub> the eddy thermal [[diffusion coefficient]] (or [[eddy conductivity]]), and Γ represents the [[adiabatic lapse rate]]. Similarly, eddy [[momentum flux]] is represented by <blockquote>[[File:ams2001glos-Ee5.gif|link=|center|ams2001glos-Ee5]]</blockquote> where ''U'' represents the mean speed in the direction of the mean wind, and ''K''<sub>''m''</sub> represents the eddy viscosity coefficient (or [[eddy viscosity]]). Also, the turbulent transfer of [[water vapor]] may be expressed in [[energy]] units by <blockquote>[[File:ams2001glos-Ee6.gif|link=|center|ams2001glos-Ee6]]</blockquote> where ''L'' represents the [[latent heat]] of [[vaporization]], ''K''<sub>''e''</sub> is the [[eddy diffusion coefficient]], and [[File:ams2001glos-Eex01.gif|link=|ams2001glos-Eex01]] is the [[specific humidity]]. <br/>''See also'' [[diffusion]], [[turbulence]].<br/> Fleagle, R. G., and J. A. Businger 1980. An Introduction to Atmospheric Physics. 2d ed., Academic Press, . 266– 272. | |||
}} | |||
= | }} | ||
Latest revision as of 06:26, 29 March 2024
(Or turbulent flux.) The rate of transfer of a conservative fluid property through a surface by turbulent eddies.
In the case of an unchanging mean state, the eddy flux of a property S in the z direction is expressed by 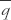 is the specific humidity.
is the specific humidity.
See also diffusion, turbulence.
Fleagle, R. G., and J. A. Businger 1980. An Introduction to Atmospheric Physics. 2d ed., Academic Press, . 266– 272.
where lower case represents turbulence values (fluctuations from the mean), w represents vertical velocity, ρ density, and the bar represents the mean over a chosen period. By analogy with molecular diffusion, the eddy flux in the planetary boundary layer is often expressed by
where Ks is the turbulent transfer coefficient (also turbulent exchange coefficient, or eddy diffusivity). This can be generalized to include eddy diffusion in the horizontal (x, y) plane. If S is replaced by cpT, where cp represents specific heat at constant pressure and T represents temperature, the vertical turbulent heat flux (or eddy heat flux) can be represented by
where θ is the temperature fluctuation, Kh the eddy thermal diffusion coefficient (or eddy conductivity), and Γ represents the adiabatic lapse rate. Similarly, eddy momentum flux is represented by
where U represents the mean speed in the direction of the mean wind, and Km represents the eddy viscosity coefficient (or eddy viscosity). Also, the turbulent transfer of water vapor may be expressed in energy units by
where L represents the latent heat of vaporization, Ke is the eddy diffusion coefficient, and
See also diffusion, turbulence.
Fleagle, R. G., and J. A. Businger 1980. An Introduction to Atmospheric Physics. 2d ed., Academic Press, . 266– 272.
