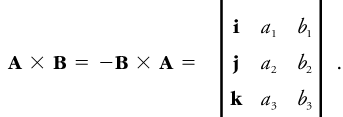vector product
From Glossary of Meteorology
(Also called cross product, outer product.) A vector with magnitude equal to the product of the magnitudes of any two given vectors and the sine of the angle between their positive directions.
For two vectors A and B, the vector product is often written A × B (read "A cross B"), and defines a vector perpendicular to both A and B and so directed that a right-hand rotation about A × B through an angle of not more than 180° carries A into B. The magnitude of A × B is equal to twice the area of the triangle of which A and B are coterminous sides. If the vector product is zero, either one of the vectors is zero or the two are parallel. When A and B are written in terms of their components along the x, y, and z axes of the rectangular Cartesian coordinates, that is,
See scalar product.
then the vector product is the determinant
See scalar product.