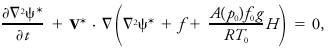equivalent barotropic model
From Glossary of Meteorology
An enhanced form of barotropic model in which the variation of wind with height is vertically averaged assuming that the thermal wind is in the same direction as the geostrophic wind at all heights.
The resulting single-parameter model for geostrophic streamfunction is
which resembles the barotropic vorticity equation except for the third term inside the brackets. ψ* and V* are the vertically averaged geostrophic streamfunction and geostrophic wind, respectively. The coefficients p0, f0, T0, g, and R are customary parameters and are defined at a reference latitude at the lower boundary. A is a vertical averaging coefficient also defined at the lower boundary. H is the terrain height, allowing the equivalent barotropic model to represent orographic forcing in a crude way. This makes the equivalent barotropic model the most popular barotropic model for real data numerical forecasts.