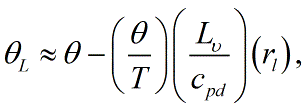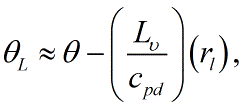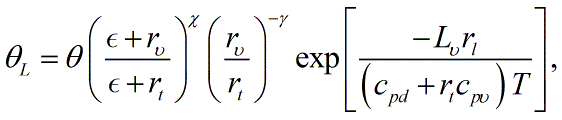Liquid water potential temperature: Difference between revisions
(Created page with " {{TermHeader}} {{TermSearch}} <div class="termentry"> <div class="term"> == liquid water potential temperature == </div> <div class="definition"><div class="short_defi...") |
m (Rewrite with Template:Term and clean up) |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
A quantity that is conserved in reversible [[adiabatic]] motion.<br/> | |||
This is typically approximated as <blockquote>[[File:Liquid_water_PT1.GIF|link=|center|Liquid_water_PT1]]</blockquote> where ''θ'' is the [[potential temperature]], ''T'' is the [[temperature]], ''L''<sub>''υ''</sub> is the [[latent heat]] of [[vaporization]], ''c''<sub>''pd''</sub> is the [[specific heat]] of [[dry air]] at constant [[pressure]], and ''r''<sub>''l''</sub> is the [[liquid water mixing ratio]].<br/> | |||
This is sometimes further approximated as <blockquote>[[File:Liquid_water_PT2.GIF|link=|center|Liquid_water_PT2]]</blockquote> where it is often assumed that ''θ''/''T'' is approximately equal to one (1), for example, for mixing processes in boundary layer clouds.<br/> | |||
< | A more accurate expression is <blockquote>[[File:Liquid_water_PT3.GIF|link=|center|Liquid_water_PT3]]</blockquote> in which ''χ'' is the [[Poisson constant]], ''ε'' is the ratio of the gas constants of dry air and [[water vapor]] (0.622), ''r''<sub>''υ''</sub> is the mixing ratio of water vapor, ''c''<sub>''pυ''</sub> is the specific heat of water vapor, ''T'' is the [[temperature]], and ''γ'' = ''r''<sub>''t''</sub>''R''<sub>''υ''</sub>/(''c''<sub>''pd''</sub> + ''r''<sub>''t''</sub>''c''<sub>''pυ''</sub>), where ''r''<sub>''t''</sub> is the [[total water mixing ratio]] and ''R''<sub>''υ''</sub> the [[gas constant]] for water vapor. Three quantities are conserved in reversible adiabatic motion: [[equivalent potential temperature|equivalent potential temperature]], total water mixing ratio, and liquid water potential temperature. Any two of these may be considered independent, with the third deducible from those two.<br/> | ||
Betts, A. K., 1973: Non-precipitating cumulus convection and its parameterization. ''Quart. J. Roy. Met. Soc.'', '''99''', 178–196<br/> | |||
Emanuel, K. A., 1994: ''Atmospheric Convection''. Oxford Univ. Press, 580 pp. <br/> | |||
<p>''Term edited 19 February 2019.''</p> | |||
Latest revision as of 05:50, 29 March 2024
A quantity that is conserved in reversible adiabatic motion.
This is typically approximated as
where θ is the potential temperature, T is the temperature, Lυ is the latent heat of vaporization, cpd is the specific heat of dry air at constant pressure, and rl is the liquid water mixing ratio.
This is sometimes further approximated as
where it is often assumed that θ/T is approximately equal to one (1), for example, for mixing processes in boundary layer clouds.
A more accurate expression is
in which χ is the Poisson constant, ε is the ratio of the gas constants of dry air and water vapor (0.622), rυ is the mixing ratio of water vapor, cpυ is the specific heat of water vapor, T is the temperature, and γ = rtRυ/(cpd + rtcpυ), where rt is the total water mixing ratio and Rυ the gas constant for water vapor. Three quantities are conserved in reversible adiabatic motion: equivalent potential temperature, total water mixing ratio, and liquid water potential temperature. Any two of these may be considered independent, with the third deducible from those two.
Betts, A. K., 1973: Non-precipitating cumulus convection and its parameterization. Quart. J. Roy. Met. Soc., 99, 178–196
Emanuel, K. A., 1994: Atmospheric Convection. Oxford Univ. Press, 580 pp.
Term edited 19 February 2019.