Speed of sound: Difference between revisions
From Glossary of Meteorology
No edit summary |
m (Rewrite with Template:Term and clean up) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Term | |||
|Display title=speed of sound | |||
{{ | |Definitions={{Definition | ||
|Num=1 | |||
|Meaning= | |||
#(Also velocity of sound.) Usually taken to mean the [[phase speed]] of an acoustic (or [[sound wave|sound]]) wave.<br/> In an ideal, stationary gas the speed of sound ''c'' is a thermodynamic property depending only on the [[equilibrium]] state of the gas and is given by <blockquote>[[File:ams2001glos-Se45.gif|link=|center|ams2001glos-Se45]]</blockquote> where γ is the ratio of [[specific heat]] capacities, at constant [[pressure]] and volume, respectively; ''R'' is the [[gas constant]]; and ''T'' is [[absolute]] temperature.<br/> | |||
#In [[seawater]], a function of [[temperature]], [[salinity]], and [[pressure]]. | |||
}} | |||
}} | |||
# | |||
# | |||
Latest revision as of 06:45, 30 March 2024
- (Also velocity of sound.) Usually taken to mean the phase speed of an acoustic (or sound) wave.
In an ideal, stationary gas the speed of sound c is a thermodynamic property depending only on the equilibrium state of the gas and is given by
where γ is the ratio of specific heat capacities, at constant pressure and volume, respectively; R is the gas constant; and T is absolute temperature.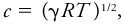
- In seawater, a function of temperature, salinity, and pressure.
