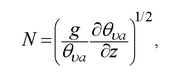Brunt-väisälä frequency: Difference between revisions
Ametsocadmin (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
|||
| (8 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{DISPLAYTITLE:Brunt-Väisälä frequency}} | |||
The [[frequency]] ''N'' at which a displaced [[air parcel]] will oscillate when displaced vertically within a [[static stability|statically stable]] environment.<br/> It is given as <blockquote>[[File:Brunt_V_final.png|170px|center]]</blockquote> where ''g'' = 9.8 m s<sup>-1</sup> is gravitational [[acceleration]], ''θ''<sub>''υa''</sub> is the ambient virtual potential temperature, and ∂''θ''<sub>''υa''</sub>/∂''z'' is the vertical [[gradient]] of the ambient [[virtual potential temperature]]. Units are radians per second, although this is usually abbreviated as s<sup>-1</sup>. This frequency is not defined in statically [[unstable air]] and is zero in statically neutral air. The frequency of internal [[gravity waves]] in the [[atmosphere]] cannot exceed the local Brunt–Väisälä frequency. This frequency is also sometimes used as a measure of the [[stability]] within a statically stable environment.<br/> | |||
<br/>''See also'' [[buoyancy frequency]].<br/>Reference:Stull, R. B. 1995. Meteorology Today for Scientists and Engineers. 385 pp. <br/> | |||
''term edited 15 Dec 2014'' | |||
== frecuencia de Brunt–Väisälä == | |||
Es la frecuencia ''N'' a la que una parcela de aire desplazada oscilará cuando se desplaza verticalmente dentro de un ambiente estable estáticamente. | |||
'' | Descrita por <blockquote>[[File:Brunt_V_final.png|170px|center]]</blockquote> | ||
donde ''g'' = 9.8 m s<sup>-1</sup> es la aceleración gravitacional, ''Tv'' es la temperatura virtual absoluta promedio y ∂θ''v''/∂''z'' es el gradiente vertical de la temperatura potencial virtual. Las unidades están en radianes por segundo, aunque por lo general, se abrevian como s-1. Esta frecuencia no se define en el aire estáticamente inestable y es cero en el aire estáticamente neutro. La frecuencia de las ondas gravitacionales internas en la atmósfera no puede exceder la frecuencia de Brunt-Väisälä local. Algunas veces se usa esta frecuencia como una medida de la estabilidad dentro de un entorno estáticamente estable. | |||
''Consulte'' frecuencia de empuje hidrostático. | |||
Latest revision as of 09:32, 19 April 2024
The frequency N at which a displaced air parcel will oscillate when displaced vertically within a statically stable environment.
It is given as
where g = 9.8 m s-1 is gravitational acceleration, θυa is the ambient virtual potential temperature, and ∂θυa/∂z is the vertical gradient of the ambient virtual potential temperature. Units are radians per second, although this is usually abbreviated as s-1. This frequency is not defined in statically unstable air and is zero in statically neutral air. The frequency of internal gravity waves in the atmosphere cannot exceed the local Brunt–Väisälä frequency. This frequency is also sometimes used as a measure of the stability within a statically stable environment.
See also buoyancy frequency.
Reference:Stull, R. B. 1995. Meteorology Today for Scientists and Engineers. 385 pp.
term edited 15 Dec 2014
frecuencia de Brunt–Väisälä[edit | edit source]
Es la frecuencia N a la que una parcela de aire desplazada oscilará cuando se desplaza verticalmente dentro de un ambiente estable estáticamente.
Descrita por
donde g = 9.8 m s-1 es la aceleración gravitacional, Tv es la temperatura virtual absoluta promedio y ∂θv/∂z es el gradiente vertical de la temperatura potencial virtual. Las unidades están en radianes por segundo, aunque por lo general, se abrevian como s-1. Esta frecuencia no se define en el aire estáticamente inestable y es cero en el aire estáticamente neutro. La frecuencia de las ondas gravitacionales internas en la atmósfera no puede exceder la frecuencia de Brunt-Väisälä local. Algunas veces se usa esta frecuencia como una medida de la estabilidad dentro de un entorno estáticamente estable.
Consulte frecuencia de empuje hidrostático.