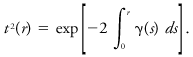lidar equation
From Glossary of Meteorology
An equation, which may appear in different forms depending on the particular system or application, that describes the relation between the received power p measured in a lidar receiver channel from range r, and the characteristics of the lidar system and the transmission medium (usually the atmosphere) through which the laser pulse propagates.
The most common form of the equation is for plane-polarized radiation and single scattering, for which
Compare radar equation.
where β is the volume backscattering coefficient at range r, t2 is the two-way transmittance to range r, and C is the lidar constant, which depends on such system parameters as the transmitted power, pulse duration, and receiver characteristics. The transmittance is related to the volume extinction coefficient γ by
Normally scattering and extinction of the lidar beam are caused by the combined effects of molecules, aerosols, and hydrometeors, so that β and γ represent the sum of their separate contributions.
Compare radar equation.