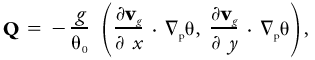Q vector
From Glossary of Meteorology
A horizontal vector, arising in quasigeostrophic and semigeostrophic theory, the divergence of which appears on the right-hand side of the omega equation.
In the context of ''f''-plane (i.e., the Coriolis parameter f is assumed constant) quasigeostrophic theory, the Q vector is defined as
In the context of ''f''-plane (i.e., the Coriolis parameter f is assumed constant) quasigeostrophic theory, the Q vector is defined as
where g is the acceleration of gravity, θ0 a constant reference value of the potential temperature, vg the horizontal geostrophic wind, ∇p the horizontal gradient operator on a constant-pressure surface, and θ the potential temperature. In the context of f-plane semigeostrophic theory, the definition of the Q vector is identical except that the physical coordinates (x, y) are replaced by the geostrophic coordinates (X, Y). The Q vector tends to point in the direction of rising air. If Q points toward warm air, the geostrophic flow is frontogenetic. If Q points toward cold air, the geostrophic flow is frontolytic.