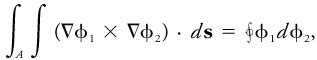solenoid
From Glossary of Meteorology
A tube formed in space by the intersection of unit-interval isotimic surfaces of two scalar quantities.
The number of solenoids enclosed by a space curve is therefore equal to the flux of the vector product of the two gradients through a surface bounded by the curve, or
See also baroclinity, vorticity equation, circulation theorem.
where ds is the vector element of area of a surface bounded by the given curve. Solenoids formed by the intersection of surfaces of equal pressure and density are frequently referred to in meteorology. A barotropic atmosphere implies the absence of solenoids of this type, since surfaces of equal pressure and density coincide.
See also baroclinity, vorticity equation, circulation theorem.