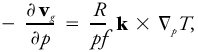thermal wind equation
From Glossary of Meteorology
An equation for the vertical variation of the geostrophic wind in hydrostatic equilibrium, which may be written in the form
This equation shows that the geostrophic wind shear -∂vg/∂p is a vector parallel to the isotherms in such a sense that the cold air is on the left of the shear (in the Northern Hemisphere). The geostrophic wind at the top of an atmospheric layer may be considered the sum of the wind at the bottom of the layer and the thermal wind determined by the mean isotherms within the layer, that is, by the thickness pattern of the layer.
where vg is the vector geostrophic wind, p the pressure (used here as the vertical coordinate), R the gas constant for air, f the Coriolis parameter, k a vertically directed unit vector, and ∇p the isobaric del operator.
This equation shows that the geostrophic wind shear -∂vg/∂p is a vector parallel to the isotherms in such a sense that the cold air is on the left of the shear (in the Northern Hemisphere). The geostrophic wind at the top of an atmospheric layer may be considered the sum of the wind at the bottom of the layer and the thermal wind determined by the mean isotherms within the layer, that is, by the thickness pattern of the layer.